How do QR codes work?
Hey Explorers, Happy Thursday!
Let’s look at how QR codes work this week. I aim to write my newsletter issues in a way one can follow them while traveling on a bus, having a coffee, waiting for food, etc. Let's jump in!
How it works: 15-second answer
A QR code encodes data, such as a URL, into a grid of black and white squares. When scanned by a phone camera, the code is decoded into readable information. Key components include square markers for edge detection, mode indicators for data type, total character count of information to be decoded, the actual encoded data, stop indicators, and error correction data.
How do QR codes work?
QR codes and barcodes essentially do the same thing. The barcode encodes the data linearly using black and white stripes. Whereas, QR codes encode data two-dimensionally using black and white squares.
What is the basic idea behind a QR code?
A QR code encodes a website URL like www [dot] google [dot] com into a series of black and white squares laid out on the square.
So, when we scan the QR code from our phone camera, this URL is decoded by the app by converting the black and white squares into a URL. But how is that possible? Let’s take a very simple example and go over this.
Figure 1: The difference between a barcode and a QR code is that barcode is linear whereas QR codes encode information in two dimensions.
Let’s say we represent the alphabets A, B, and C as a combination of 1s and 0s. And let’s assume that our camera QR code scanner already knows that each alphabet is represented by 4 numbers.
A = 1001
B = 0010
C = 1111
Now if I want to form the word ‘CAB’, then we can write “1111 1001 0010”
If we want to encode this, we can represent this numeric string as a series of black and white squares, where black squares represent the number 0 and the white squares represent the number 1. This is what the word CAB looks like in terms of black and white squares.
Figure 2: Black and white square notations for the word CAB as per our example. (Black squares are 0s and White squares are 1s)
Instead of laying it out in a straight line, if we wind it around like we go over the square board on a snake and ladder game, then we have the QR code ready. But there are more components to a QR code than just encoding the URL which we will see in the next section.
Note: The representation we gave for the letters A, B, and C and the way the QR code is generated here is only an example and not the exact method. The original protocol is different. But you get the idea. Now let’s see what are the different components of a QR code and what is it that we are scanning every time.
Different components of a QR code
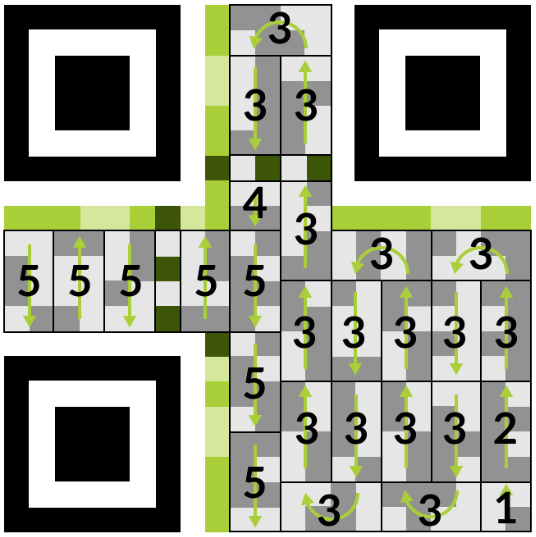
When you use your phone’s camera to scan a QR code, it first recognizes three square markers at the corners that help it find the edges of the QR code.
Figure 3: Components of a QR code (Source: Sprout)
All the following information is encoded in the form of black and white squares as we discussed in the previous section.
What is the type of data encoded - Marked as 1 in the figure.
Starting at the bottom right, the scanner finds the mode indicator, which tells it what type of data is in the QR code (numeric, alphanumeric, etc).Total number of characters to scan - Marked as 2 in the figure.
Next, the scanner reads the character count indicator, which tells it how many characters are in the encoded data.Encoded URL information to be opened - Marked as 3 in the figure.
With the data type and character length known, the scanner follows a zig-zag path to read all the encoded information until it reaches the end. This has the URL information to be opened in it.Stop indicator - Marked as 4 in the figure.
This shows that the encoded data needed to scan the URL is complete.Error correction data - Marked as 5 in the figure.
After reading all the data, the scanner checks the error correction data. This data helps recover the information if the QR code is damaged.
These are the components that make a QR code possible. And this is why it works as smoothly as butter, every single time. Now you and I know what we’re getting into the next time we come across a QR code!
Question of the week
What do the green lines around the three corner position marker squares in Figure 3 represent? Reply to this email with your thoughts, and we’ll discuss.
That's all folks. Thank you for reading!
Have an amazing rest of the week, and take care!
Until next to next Wednesday,
Chendur