How do Pacemakers work?
Hey friends, Happy Wednesday Thursday!
Last week, I sent out the newsletter issue on the best 200 inventions of 2022 released by TIME magazine. This week, we’ll look at how pacemakers work. It is a small device that's placed (implanted) in the chest that sends electrical pulses to help your heart beat at a normal rate and rhythm. I aim to write my newsletter issues in a way one can follow them while traveling on a bus, having a coffee, waiting for food, etc. Let's jump in!
How does your heart work? 101
The chambers at the top of the heart are the right and left atriums. The ones in the bottom are the right and left ventricles.
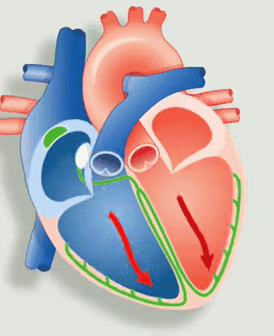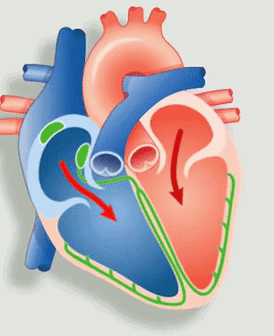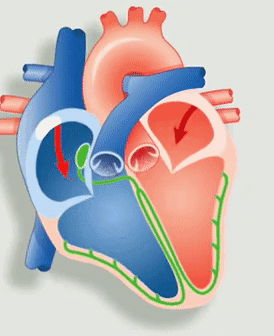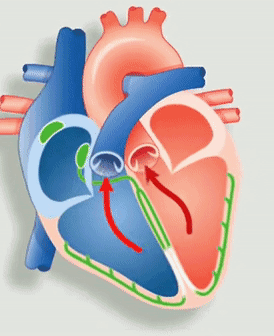
Figure 1: Animation of the heart’s electrical system. Source: Economist
The deoxygenated blood from the body flows into the right atrium and oxygenated blood from the lungs flows into the left atrium. An electrical signal from the sinoatrial node (the green node not connected to any fibers in Figure 1.) causes the atrium to contract. Thus, opening the one-way valve for the blood to flow to the right and left ventricle chambers respectively.
Now, the electrical signal from the atrioventricular node (the green node connected to fibers in Figure 1) causes the ventricles to contract, thereby pushing the blood from the right ventricle to the lungs and from the left ventricle to the body.
Why do we need Pacemakers?
Electricity drives every beat of our hearts. A bundle of nerves at the heart (the green nodes in Figure 1) is an electrical generator. Nerves, functioning as wires, transmit messages to the lower chambers of your heart, telling it when to contract. A slow heart rate can prevent the heart from pumping enough oxygen-rich blood, and can even cause serious conditions such as heart failure or even death. Hence, we use a computerized device called a Pacemaker that makes sure that the heart beats at the required beats per minute.
How do pacemakers work?
Traditional pacemakers have three main parts.
Figure 2: Pacemaker placed in a human body
A pulse generator creates electrical pulses. It is a small metal case that contains electronic circuitry with a small computer and a battery that regulates the impulses sent to the heart.
Wires are implanted inside the veins and carry the pulses to your heart. It is connected to the pulse generator on one end, with the other end placed inside one of the heart’s chambers.
Electrodes deliver electrical impulses to your heart to make it beat normally. The electrode on the end of a lead touches the heart wall. The lead delivers electrical impulses to the heart. These signals cause stimulation of the heart muscle making them contract. Thus, the heart functions naturally by contracting at the right pace through artificial pacemakers. We found in the previous section that it's the squeezing of heart muscles through an electrical activity that causes the blood to be pushed into different chambers.
A traditional pacemaker generator is placed outside of your heart, either in your chest or abdomen. The pacemaker sends electrical signals only when the natural heartbeat is not optimal. The data is stored in the pacemaker which the doctor can review for post-processing and can also adjust the settings if needed. There have been further developments like using wireless pacemakers and many other different models. But the big picture has been the same, generating electrical signals :)
Question of the week
What do you think are the negative impacts of using a pacemaker? Share your thoughts by replying to this email, and we can have a discussion. I’ll answer this in next week’s issue.
Blog posts
I’ll include the essence of every blog post on how gadgets work in my newsletters moving forward. I’ll also attach the link to the blog post if you’d like to read the extended version as usual.
My blog post S1E9 for Season 1: Wellness Gadgets is due! I’ll catch up with it, now that I’m back on the ground after my vacation :P
Glad I was able to find time to write newsletters every week even during my vacation. Let me know if you’d like to read about a specific gadget/device.
Gadget of the week!
Exodigo Subsurface Mapping Platform for Underground Exploration: The drilling required to find out what’s underground is expensive and causes a lot of damage to the environment. So Exodigo offers a platform to use radar, LIDAR, and other sensors to scan the ground to produce detailed 3D subsurface maps. These can be used in turn for making decisions by miners, construction companies, etc.
Thank you for reading. Have a nice rest of the week, and take care!
Until next Wednesday,
Chendur